110/68 Thursday, March 20, 2025
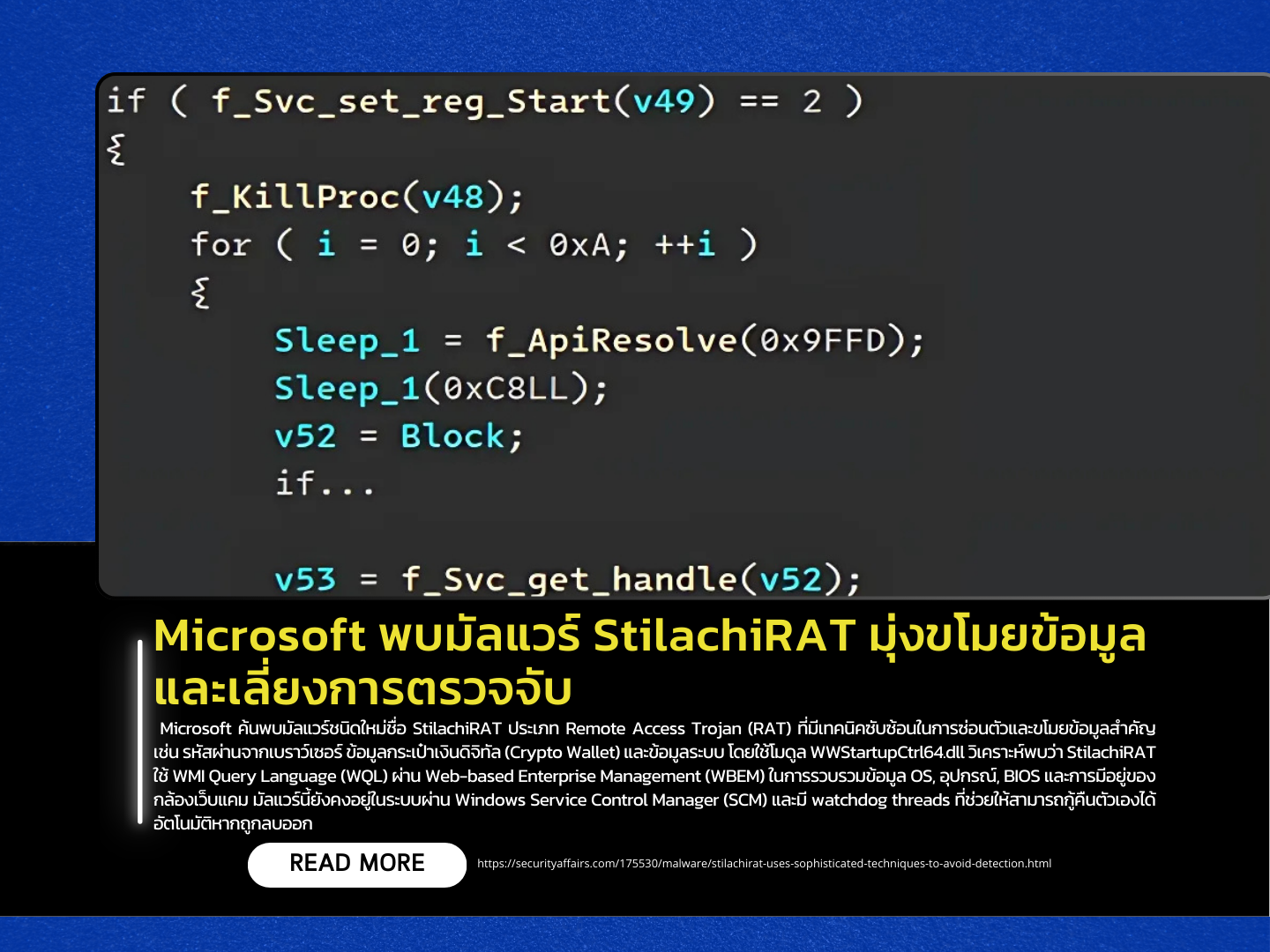
Microsoft has identified a new malware strain called StilachiRAT, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) with advanced techniques for hiding itself and stealing sensitive data such as browser passwords, cryptocurrency wallet information, and system details. The malware leverages the WWStartupCtrl64.dll module and utilizes WMI Query Language (WQL) through Web-based Enterprise Management (WBEM) to gather data about the operating system, hardware, BIOS, and webcam presence. StilachiRAT persists within the system using the Windows Service Control Manager (SCM) and employs watchdog threads, enabling it to automatically restore itself if deleted.
StilachiRAT can steal data from over 20 cryptocurrency wallet extensions, including MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet, and TronLink. It extracts the encryption_key from Google Chrome and uses Windows API calls to decrypt stored passwords, then transmits the stolen information to a command-and-control (C2) server. The malware encrypts IP addresses in binary format and randomly selects ports 53, 443, or 16000 to evade detection. Additionally, StilachiRAT monitors RDP sessions to impersonate users and spread attacks within a network.
To avoid detection, the malware clears system logs, checks for analysis tools, and replaces API names with checksum values. Microsoft reports that StilachiRAT supports various C2 commands, including system reboots, log deletion, data theft, application control, and network connections. It also features specific commands for extracting passwords from Google Chrome, indicating its focus on credential theft and remote system control. In response, Microsoft has released Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and mitigation guidelines to help organizations detect and defend against this malware.
